Blog / Automated Data Mapping: Benefits and Use Cases
Automated Data Mapping: Benefits and Use Cases
Automated data mapping is reshaping how businesses in the GCC manage and integrate data from diverse systems. By using AI tools, it eliminates manual coding, speeds up data integration, and ensures compliance with local regulations like the UAE Smart Data Framework and Saudi Arabia’s PDPL. This approach is vital for handling multilingual data and scaling operations efficiently.
Key takeaways:
- Faster integration: Reduces timelines from weeks to hours.
- Improved accuracy: Minimises human errors with AI-driven precision.
- Scalability: Handles growing data volumes and evolving systems seamlessly.
- Compliance: Aligns with GCC data protection laws and frameworks.
For GCC businesses, automated mapping is crucial for unifying fragmented data, enabling better decision-making, and supporting personalised marketing strategies. Tools leveraging AI and rule-based logic simplify complex tasks, making them suitable for enterprises managing vast datasets across multiple markets. This technology is transforming data integration into a streamlined, efficient process.
AI Data Mapping Explained: Benefits and Tips
Benefits of Automated Data Mapping
Automated data mapping brings three key advantages for businesses in the GCC: faster integration, improved accuracy, and the ability to scale efficiently.
Faster Data Integration
Manual data mapping can stretch integration timelines from weeks to months. In contrast, automated tools significantly reduce this timeframe, completing tasks in just hours. Businesses using automated platforms report up to 10x higher productivity compared to traditional methods. This speed is especially critical in the GCC, where companies often operate in multiple markets and must adapt quickly to changing regulations and customer needs.
Many automated systems also feature real-time discovery of new data sources and schema updates. This eliminates the hassle of manually rebuilding pipelines when systems evolve [12, 16]. Considering that the average office worker now uses over 11 different applications, manual integration quickly becomes unmanageable for IT teams. By accelerating integration, businesses can also achieve better accuracy and scalability across their operations.
Better Accuracy and Data Quality
Manual data mapping is prone to human error, often caused by spreadsheet-based processes. Automated systems solve this problem by ensuring precise field alignment, removing the risk of mistakes [10, 12]. Machine learning capabilities in these tools can even identify and link semantically similar fields with different names - like matching "ShipCountry" with "ShipNation".
Real-time validation features further enhance accuracy, allowing data teams to debug complex mappings immediately and prevent errors from entering the workflow. This is particularly important for compliance with frameworks like the UAE Smart Data Principle and Standards, which set guidelines for data classification and schema specifications to ensure information is reliable and fit for use. Such precision is vital for large organisations aiming to scale their operations effectively.
Scaling for Large Enterprises
As data volumes and sources grow, manual mapping often leads to "blind spots" that can result in compliance issues or inconsistent reporting [10, 12]. Automated mapping tools are built to handle dynamic scaling, enabling GCC businesses to integrate new applications, databases, and APIs without overhauling existing pipelines.
Regional case studies highlight how automated systems manage complex datasets with ease. They also simplify mergers and acquisitions by automatically identifying overlapping fields and resolving conflicts in combined data landscapes. These tools are designed to handle intricate schemas and high-frequency data transfers that would be nearly impossible to manage manually. This makes it easier for organisations to move from small-scale pilot projects to full-scale deployments [10, 1]. Moreover, this approach aligns with the UAE Smart Data Principle, which emphasises making data "reusable by default" to ensure seamless interoperability between entities and external partners.
How Automated Data Mapping Works
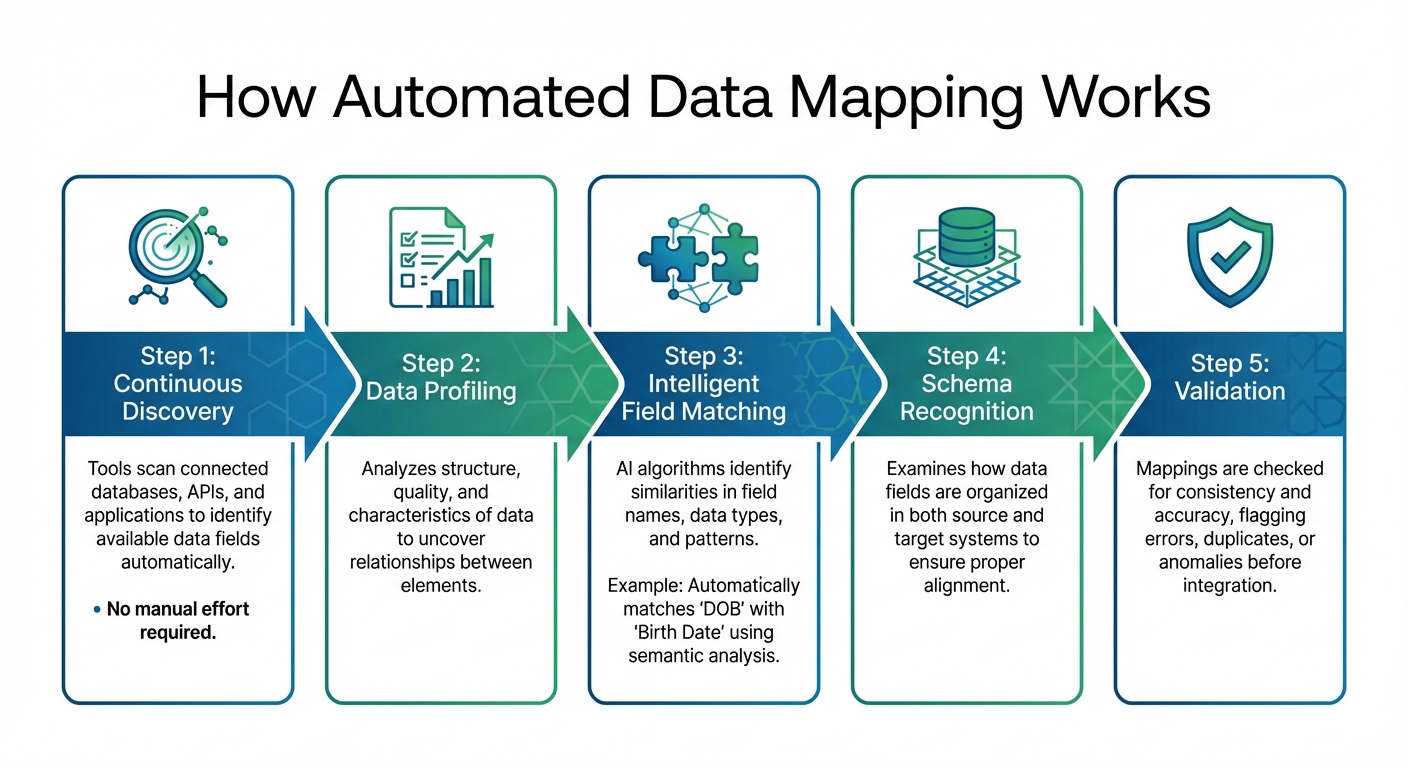
5-Step Automated Data Mapping Process: From Discovery to Validation
Automated data mapping is transforming how data integration is handled in the GCC. The process begins with continuous discovery, where tools scan connected databases, APIs, and applications to identify available data fields - no manual effort required. Next comes data profiling, which analyses the structure, quality, and characteristics of the data to uncover relationships between different elements.
At the heart of the process is intelligent field matching, where AI algorithms identify similarities in field names, data types, and patterns. For example, the system can automatically match "DOB" with "Birth Date" using semantic analysis. Then, schema recognition examines how data fields are organised in both the source and target systems to ensure proper alignment. The final step is validation, where mappings are checked for consistency and accuracy, flagging errors, duplicates, or anomalies before the integration takes place. This ongoing process lays the groundwork for automation and ensures data readiness for subsequent steps.
Steps in the Automated Mapping Process
The automated mapping workflow involves several key stages. After discovery and profiling, the system moves to schema recognition, which analyses structural constraints in both source and destination databases. This step is particularly useful for GCC organisations managing data across multiple jurisdictions.
Schema drift management is another critical feature, tracking real-time structural changes and automatically updating mappings to avoid the need for manual pipeline rebuilds. This is especially valuable as systems evolve. In fact, data scientists reportedly spend up to 40% of their time on manual data preparation tasks - time that automation can save.
Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in the region also play a pivotal role in data governance, acting as central hubs to maintain a single source of truth across geographically dispersed divisions. As Kunal Ghatak, Partner, Global Business Services at EY India, aptly puts it:
"The rather subtle maxim 'garbage in, garbage out' is applicable to any data analysis exercise".
AI and Rule-Based Methods
Modern data mapping systems combine AI with rule-based logic to handle both straightforward and complex tasks. Rule-based methods are ideal for deterministic tasks, such as standardising date formats or currency conversions, while AI takes on more nuanced tasks like semantic matching and pattern recognition. This combination is particularly effective for GCC businesses that work with multilingual datasets.
AI uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to interpret field labels across languages. For instance, it can understand that "Customer Name" in English and "اسم العميل" in Arabic refer to the same entity, even though the text differs. Additionally, with around 90% of organisational data being unstructured, AI is crucial for extracting and mapping this information into structured formats ready for analysis.
Machine learning models also improve through "human-in-the-loop" interactions. When users accept or reject a proposed mapping, the AI learns from this feedback to refine future suggestions for similar datasets. Meanwhile, rule-based transformations ensure compliance with frameworks like the UAE Smart Data Principle and Standards, which define specific metadata, data formats, and schemas for seamless interoperability.
| Feature | Rule-Based Mapping | AI/ML-Based Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Best Use Case | Simple tasks (e.g., date/currency conversion) | Complex or evolving schemas |
| Flexibility | Low; manual updates needed for new formats | High; adapts through pattern recognition |
| Accuracy | High for predefined rules; prone to failures | Improves over time with user feedback |
| Effort | High manual setup for complex logic | High initial setup; minimal ongoing effort |
Cloud Platform Integration in the GCC
Once the mapping process is complete, cloud integration platforms take efficiency and scalability to the next level. Platforms like Airbyte, Domo, Nexla, and Informatica provide the necessary infrastructure for automated mapping in the GCC. For example, Airbyte supports over 600 pre-built connectors and processes more than 2 petabytes of data daily. These cloud-native systems enable businesses to scale mapping automatically as data volumes grow, avoiding the manual rebuilds associated with older systems.
Incremental sync using Change Data Capture (CDC) ensures only modified records are updated, reducing latency. For GCC organisations with strict data residency requirements, hybrid deployment options allow automated mapping to be cloud-managed while keeping data processing local.
Advanced fuzzy matching algorithms also handle phonetic similarities and regional variations. For example, they can identify matches between different transliterations of Arabic names in English databases. Additionally, platforms like AWS Entity Resolution offer visual lineage tools with interactive dashboards, making it easier for non-technical stakeholders to understand how insights are derived from mapped data. This level of transparency is vital for meeting local regulations and fostering trust in automated systems across diverse teams.
sbb-itb-058f46d
Use Cases in GCC Marketing
Automated data mapping is reshaping digital marketing strategies for businesses in the GCC by turning scattered customer data into actionable insights. This innovation addresses a key challenge in the region, where only 25% of organisations have achieved advanced digital maturity, compared to a global average of 31%. By unifying data, businesses can create more targeted and effective marketing campaigns across various industries.
CDP Integration for Personalisation
In the UAE retail sector, automated data mapping plays a vital role in integrating Customer Data Platforms (CDPs). It connects customer records from websites, social media, and analytics tools, building a comprehensive, 360-degree view of each customer. This is especially relevant in the GCC, where over half of customers believe generative AI enhances their online and in-store shopping experiences.
The accuracy provided by data mapping is critical, considering that 83% of companies struggle with inaccurate data, often leading to poor decision-making. For GCC retailers, addressing this issue can result in personalised experiences that boost revenues by 5% to 7%. Wick's Capture & Store pillar utilises automated mapping to unify customer data, enabling AI-driven personalisation tailored to the region. This includes managing multilingual datasets and adhering to the UAE Smart Data Framework.
Marketing Automation Data Alignment
With unified customer data in place, automated mapping simplifies marketing campaigns by aligning data from tools like SEO platforms, paid advertising systems, and CDPs. It connects customer records across CRMs, marketing platforms, and billing systems, enabling automated triggers such as cart abandonment recovery or personalised offers based on real-time customer behaviour.
Identity resolution is another key benefit, linking customer identities across devices and platforms to avoid redundant messaging.
"The power of a CDP lies in its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights, driving tailored marketing that resonates with each unique customer".
Wick's Tailor & Automate pillar uses automated mapping to synchronise diverse data sources, ensuring campaigns targeting Saudi audiences are both effective and compliant with regional standards. These efforts, part of Wick's Four Pillar Framework, show how automated mapping improves personalisation and campaign efficiency. Financial institutions in the GCC, which lead in AI maturity with 29% achieving top-tier levels in 2024, are already benefiting from these advancements.
Customer Journey Mapping for Enterprises
For large enterprises in Qatar and across the GCC, understanding customer journeys across multiple digital touchpoints - like website visits and post-purchase interactions - is essential. Automated data mapping connects fragmented databases through continuous discovery, eliminating gaps that manual systems often leave behind. This ensures customer journey maps remain up-to-date without requiring constant manual intervention.
The technology also enables visual data lineage, making it easier for non-technical marketing teams to understand how customer insights are generated. Before automation, 82% of master data management survey respondents reported spending at least one day a week resolving data quality issues manually. For financial enterprises in Qatar, automated mapping opens the door to predictive analytics, helping them anticipate customer needs.
"GCC organizations show higher maturity around customer journey and digital operations capabilities, however, have yet to fully possess many of the critical enabler capabilities... and will need a step-change, particularly in their data and technology capabilities".
Implementation Best Practices
Evaluate Your Data Quality First
For businesses across the GCC, ensuring top-notch data quality is a critical first step. Poor data quality can lead to losses amounting to US$12.9 million annually. To avoid such pitfalls, establish clear benchmarks for data quality that include accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, validity, and uniqueness [35, 38].
Check for data freshness, eliminate null values, and ensure referential integrity to align with the UAE Smart Data Principle and Standards, which prioritise reliability and purpose-fit data [34, 2]. Organisations that invest in improving their data quality often see revenue gains of 15–20%. Once your data quality is solid, the next step is selecting effective mapping tools.
Choose the Right Tools
The tools you choose should cater to the specific needs of the GCC region. Look for platforms that support Arabic metadata, comply with frameworks like the UAE Smart Data Standards, and utilise AI-driven pattern recognition [2, 12]. These platforms should also feature continuous discovery and visual data lineage capabilities, making it easier for non-technical teams to understand data flows.
Security is another essential factor. Ensure the tools you select include robust encryption and role-based access control to meet the Central Bank of UAE's stringent requirements [40, 41]. Additionally, confirm that the platform offers native connectors for enterprise tools like SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft Dynamics. These features not only improve mapping precision but also ensure seamless integration into your strategic frameworks.
Integration with Wick's Four Pillar Framework

Once the right tools are in place, Wick's Four Pillar Framework can help you optimise automated mapping during its Capture & Store and Tailor & Automate phases.
- In the Capture & Store phase, automated discovery eliminates manual blind spots, ensuring a robust foundation for AI-driven personalisation.
- The Tailor & Automate phase uses intelligent matching to align customer fields across CRMs and marketing platforms, creating unified profiles for personalised campaigns.
This framework also includes continuous synchronisation, which automatically adapts to changes in CRM schemas without disrupting workflows. Built-in audit trails further ensure compliance with regional data protection regulations. By combining high-quality data with the right tools and frameworks, businesses can streamline customer data management and achieve better results across GCC markets.
Conclusion
Automated data mapping has become a game-changer for businesses in the GCC striving to excel in today’s digital-first economy. While an impressive 84% of GCC organisations have embraced AI, only a small fraction - 11% - can be classified as "value realisers", meaning they generate at least 5% of their earnings from these technologies. One major roadblock? Fragmented data scattered across various systems, which hinders the creation of unified customer profiles. Automated mapping breaks down these silos, paving the way for precise personalisation, stronger customer retention strategies, and faster decision-making.
Given the sheer volume of data processed daily in the region, relying on manual, spreadsheet-driven mapping processes is no longer practical. Automation not only accelerates integration timelines - from weeks to mere hours - but also ensures compliance with local regulations, an essential factor in the GCC.
"The GCC stands at a crossroads where technological advancements intersect with the region's aspirations to lead in digital and AI innovation."
One effective approach to tackling this challenge is Wick's Four Pillar Framework, which incorporates automated mapping into its "Capture & Store" and "Tailor & Automate" phases. This strategy enables marketing teams to shift their focus from repairing broken data pipelines to engaging in rapid experimentation. By leveraging AI-powered discovery, continuous synchronisation, and built-in audit trails, this framework transforms data management from a tedious operational task into a powerful tool for driving sustainable growth across the GCC.
To make the most of these advancements, it’s crucial to prioritise high-quality data, adopt advanced mapping tools, and integrate these capabilities into a scalable, unified digital ecosystem. By doing so, businesses can turn data challenges into opportunities, unlocking new pathways for growth and innovation across the region.
FAQs
How does automated data mapping help businesses in the GCC comply with local regulations?
Automated data mapping makes meeting compliance requirements much easier by pinpointing, categorising, and documenting how data moves and is stored. This helps organisations ensure their operations align with regulations specific to the GCC, such as personal data protection laws and requirements for data to remain within certain locations.
By keeping precise records and implementing effective controls, businesses can show they meet industry standards and regulatory demands. This not only lowers potential risks but also strengthens trust with stakeholders across the region.
How does AI improve the accuracy of automated data mapping?
AI brings a new level of precision to automated data mapping by using machine learning to spot patterns, recommend precise field matches, and verify data relationships. What's more, it doesn’t stop there - AI keeps improving these mappings over time, ensuring fewer mistakes and sharper accuracy.
For businesses, this means a potential accuracy rate of up to 99.5% in data mapping. This not only simplifies workflows but also saves time and resources. In the UAE, where efficient data management plays a key role in fostering innovation and progress, these advancements are especially impactful.
What are the benefits of automated data mapping for marketing in the GCC?
Automated data mapping simplifies the task of handling and merging various customer data sources, making it faster and less prone to mistakes. For marketers in the GCC, this translates to enhanced data precision, stronger adherence to local regulations, and the capability to craft more tailored, data-focused campaigns.
With automation, businesses can bring together scattered datasets, allowing for quicker insights and smarter decisions. This holds particular importance in the UAE, where creating marketing strategies that resonate with a diverse audience is essential for driving long-term success.
